India-Mauritius bilateral relationship marks a strategic beauty with respect to maritime trade and security on Western Indo-Pacific Region (WIOR) , a fine example of diverse cultural exchange rooted in history, burgeoning opportunities for economic and socio-developmental partnerships, and shared values of democracy-cutting across party lines.
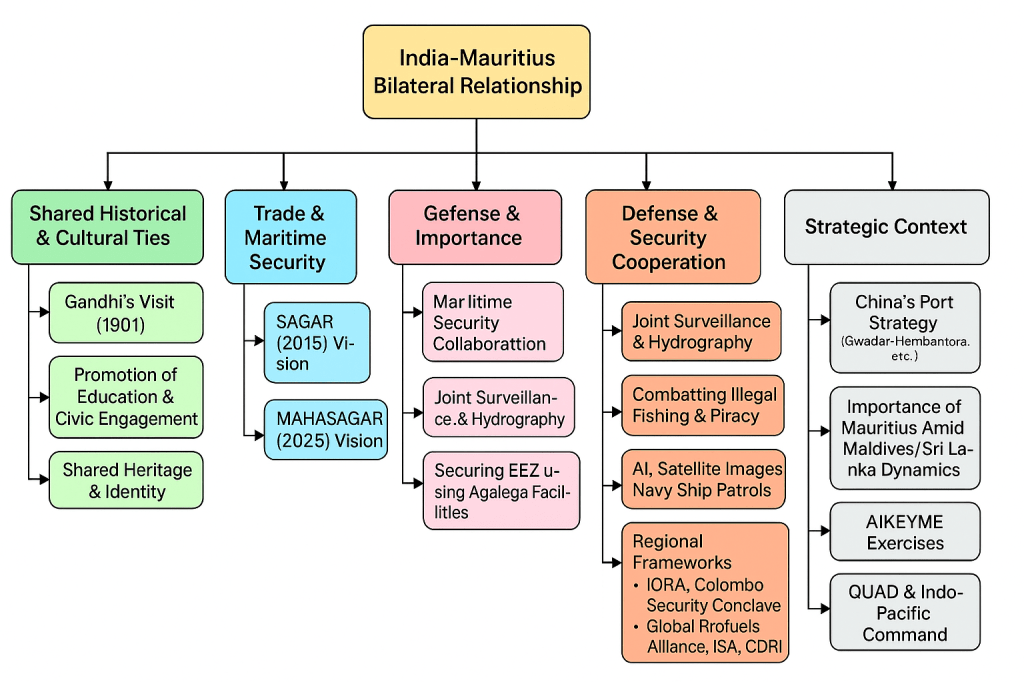
Let us begin with history, underlined by shared democratic principles and values. Mauritius’ Independence and Republic day falls on March 12th , which is also the date on which Gandhi began his Dando March in 1930. Gandhi’s deeply profound and impactful visit to Mauritius, on his way to India from South Africa , from October 29 to November 15, 1901is very significant. Through a three-pronged consisting of mainly emphasizing the importance of education as a tool for social advancement, urging the Indian-origin community in Mauritius to prioritize literacy and formal learning. He also encouraged them to engage in civic and political life to secure their rightful place in governance. Additionally, he highlighted the significance of maintaining strong cultural and emotional bonds with India, reinforcing their shared heritage and identity.
Significance of Trade and Maritime Security in Indian Ocean Region
The issue of trade and maritime security within the every dynamic geopolitical workings of Western Indo-Pacific Region (WIOR ) has indeed occupied an important place in India-Mauritius bilateral relationship. A perfect example of that would be progress fron India’s Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) vision for maritime security introduced by PM Modi in 2015 on his visit to Mauritius to Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) this year. India serves as a significant development partner to Mauritius, a relationship characterized by strong trade ties and mutually beneficial economic collaboration.The Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) between Mauritius and India has played a critical role in strengthening the economic ties between the two nations, serving as a key framework for promoting bilateral trade, facilitating market access, and deepening overall economic engagement. This brings us to the significance of the aforementioned progress. The Western Indo-Pacific region includes parts of the Indian Ocean near Africa’s east coast, the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman Sea. It also covers coastal waters around Madagascar, Seychelles, the Comoros, the Mascarene Islands, Maldives, and the Chagos Archipelago.Additionally, out of the three Archipelagos, India controls Andaman archipelago, out of Chagos Archipelago, India controls Lakshadweep (the other two excluded are Maldives and Diego Garcia) , and maintains strategically healthy relationship with Seychelles, Mauritius and the Reunion. This is precisely the reason for significantly important relationship with Mauritius. Within the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) issues of maritime security(SAGAR 2015 to MAHASAGAR 2025) , infrastructural development collaborations, defence cooperation commitments and implementations (such as Enhanced StrategicRelationship focusing on groand security), bilateral partnerships and collaboration through region specific frameworks( such as Indian Ocean Rim Association ,Colombo Security Conclave, the Global Biofuels Alliance, International Solar Alliance, and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure)are of great significance. Both the leaders affirmed their shared commitment to addressing regional threats and challenges by strengthening defense and maritime cooperation with Mauritius. They agreed to supply Mauritius with necessary defense and maritime equipment, increase joint maritime surveillance and hydrography surveys, and enhance efforts to secure Mauritius’ Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), including utilizing Agalega’s new runway and jetty. For a long time Mauritius has faced criminal activities such as illegal fishing leading to reduction in Mauritius’ fish stocks, thereby threatening its food security, and damaging the marine environment. Consequently, Mauritius has started using satellite images and AI in identification of illegal foreign fishing boats.Meanwhile, India helps by sending navy ships for joint patrols to fight piracy and illegal fishing, and by hosting the Indian Information Fusion Center, which improves maritime security by sharing information. Mauritius is one of 12 partner countries with a liaison officer at the center. They also committed to establishing a National Maritime Information Sharing Centre, offering expertise in marine operations, engineering, port safety, and security, and providing tailored training and capacity-building programs for the Mauritius Police Force.India has traditionally been the ‘First Responder’ for Mauritius in times of crisis, including during the recent Covid-19 and Wakashio oil-spill crises and this indeed an important angle to providing disaster management security infrastructure to Mauritius. In broader prudential light, given China’s control over Gwadar, Hambantota , Kyauophu, the relationship with Mauritius is of great significance. With back and forth changing landscape of relationships with Maldives and Sri Lanka, relationship with Mauritius holds even greater significance. Additionally, India has gone a step further and initiated exercises such as Africa India Key Maritime Engagement , AIKEYME. Additionally, the transition from Pacific Command to Indo-Pacific Command under Trump administration with respect to QUAD bolsters India’s efforts for maritime security with Indian Ocean Region, thereby adding impetus to existing efforts by India.
Sources
PIB
edbmauritius.org
mea.gov.in
hcimauritius.gov.in

Leave a comment